
What is Caddy and how I use it?
Caddy is an extensible platform to serve your sites, services, and apps, written in Go.
I use Caddy has a reverse proxy on my home lab, because if you want to use HTTPS with relative simplicity, Caddy does it and you do not need to use Certbot to create a certificate because it’s created automatically.
If you use Caddy at home, please ensure that the port 80(HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) is open on your router.
What is a reverse proxy?
A reverse proxy server is a server that sits between client devices and a web server, forwarding client requests to the web server.
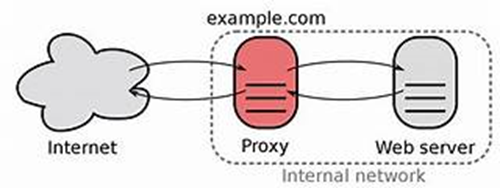
It acts as an intermediary, receiving requests from clients and then sending those requests to the appropriate server. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Client Request: A client (like a web browser) sends a request to the reverse proxy server.
- Request Forwarding: The reverse proxy server takes this request and forwards it to the appropriate web server.
- Server Response: The web server processes the request and sends a response back to the reverse proxy server.
- Response to Client: Finally, the reverse proxy server forwards the response from the web server back to the client.
Reverse proxy servers are used to enhance security, performance, and reliability of the server environment. They can provide additional functions such as load balancing, SSL encryption, and caching of static content, which can help reduce the load on web servers and improve the speed of content delivery to clients. Would you like to know more about any specific aspect of reverse proxy servers?
How to install Caddy on Ubuntu/Debian?
In my case I’m using Ubuntu/Debian servers so I will show the best I can, how to install and configure “Caddyfile” to use it has a reverse proxy.
Use the commands bellow to install caddy:
|
sudo apt install -y debian-keyring debian-archive-keyring apt-transport-https curl |
|
curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/caddy/stable/gpg.key' | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/caddy-stable-archive-keyring.gpg |
|
curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/caddy/stable/debian.deb.txt' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/caddy-stable.list |
|
sudo apt update |
|
sudo apt install caddy |
If the image bellow appears , this means you have successfully configured caddy.

Now you just need to edit the “Caddyfile” that is locate on /etc/caddy/Caddyfile and in this case configure it has a reverse proxy
$ sudo vi /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
|
# The Caddyfile is an easy way to configure your Caddy web server. # # Unless the file starts with a global options block, the first # uncommented line is always the address of your site. # # To use your own domain name (with automatic HTTPS), first make # sure your domain's A/AAAA DNS records are properly pointed to # this machine's public IP, then replace ":80" below with your # domain name.
mediaserver.home { reverse_proxy 192.168.0.100:7099
}
mylocalblog.home { reverse_proxy localhost:80 }
# Refer to the Caddy docs for more information: # https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile
|
For more information, please refer to: Caddy Install and configuration.